To evaluate or examine an object through the high-frequency waves, Known as Ultrasonic Testing.
Introduction-
Ultrasonic Testing(UT) is a method of Non-Destructive Testing, where high-frequency sound waves are used to test material or objects.
It is employed in a variety of industries, including the manufacturing, aerospace, automotive, and other transportation sectors, as well as the construction of steel and aluminum structures.
In this article, you are going to get a complete analogy of Ultrasonic Testing, Where I will start from Scratch and reach the depth of this testing,
I can assure you, that I will get complete knowledge in one place and at your fingertips.
So, Come with me and I will take you on the knowledgeable journey of UT.
What is Ultrasonic Testing?
As I discussed earlier, To evaluate or examine an object through high-frequency waves is known as Ultrasonic Testing.
Where Ultrasonic waves of frequency range 0.5MHz to 20MHz are used for the testing of materials. The most common range for testing metals is from 2MHz to 5MHz. These sound waves are higher than the human capacity range of hearing.
Principle of Ultrasonic Testing–
As you know, UT is an NDT method that uses high-frequency sound waves to conduct or evaluate the test piece.
Where A receiver generates high-voltage electrical pulses and a transducer converts those electrical pulses to high-frequency ultrasonic waves.
These waves propagate through the object in the form of sound waves.
If there is any defect or discontinuity in the path of sound waves, those waves reflect back to the receiver, Where the transducer converts Sound waves to electrical waves and displays them on the screen.
The image below is the best way to understand easily. Have a look…

How Ultrasonic Testing Works?–
A transducer converts electrical waves into high-frequency sound waves, which propagate inside the test object.
When sound waves encounter any discontinuity in its path, they reflect back to the receiver, where sound waves are converted to electrical waves and displayed on an oscillator display.
A couplant(water or oil) is used to maintain the seamless propagation of Sound waves.
UT made it possible to detect thickness, cracks, or other defects by analyzing the graph, displayed on the oscillator display.

Types of Ultrasonic Testing-
There are several types of UT, which are used in required sectors, Given below-
- Automated Ultrasonic Backscatter Technique(AUBT)
- Phased Array Ultrasonic Testing(PAUT)
- long Range Ultrasonic Testing(LRAUT)
- Internal Rotating Inspection Systems(IRIS)
- Time of Flight Diffraction(TOFD)
- Dry-Coupled Ultrasonic Testing(DCUT)
- Rapid Ultrasonic gridding(RUG)
To know more details about these types of UT Click here- 10 Different Types of Ultrasonic Testing
Methods of Ultrasonic Testing-
Some of the UT methods are illustrated below-
- Pulse-Echo Testing
- Through-Transmission Testing
1. Pulse-Echo Testing–
This method is most commonly utilized in the ultrasonic testing of materials. The transmitter and receiver probes are on the same side of the specimen and the presence of a defect is indicated by the reception of an echo before that of the back wall echo.
The CRT screen is calibrated to show the separation in distance between the time of arrival of a defect echo and that of the back wall echo of the specimen. Therefore, the location of a defect can be assessed accurately.
Fig. Principle of Pulse-Echo Method-

2. Through-Transmission Testing–
In this method, two ultrasonic probes are used. one is the transmitter probe and the other is the receiver probe. These probes are situated on the opposite side of the specimen as shown in the figure.
Fig. Position of transmitted and receiver probe in Through-Transmission testing-

In this method, the presence of an internal defect is indicated by a reduction in signal amplitude, or in the case of gross defects, complete loss of transmitted signal.
The appearance of the CRT screen is shown in the figure.
Fig. The appearance graph of through-transmission testing-

This method is used for the inspection of large ingots and casting particularly when the attenuation is high and gross defects are present.
The method does not give the size and location of the defect. In addition, good mechanical coupling and alignment of the two probes are essential.
Procedure of Ultrasonic Testing(UT)–
Here is the step-by-step procedure of Ultrasonic testing, down below-
- An object or test piece is identified to perform UT.
- Now, any oil or gel is applied to the probe to smother rubbing and clearer data.
- The probe is placed on the object, where electrical waves are converted into high-frequency sound waves.
- A sound wave is propagated through the object.
- If any flaws or defects come along the sound waves path, the waves reflect back to probe.
- Again those ultrasonic waves are converted into electrical waves and displayed on the screen.
- Further data is analyzed to give the result of testing.
What is the Ultrasonic Wave?–
Sound waves are vibrations of particles of gases, solids, or liquids. The audible sound range of frequencies is usually taken from 20Hz to 20KHz. Sound waves with frequencies higher than 20KHz are known as Ultrasonic Waves.
In general, Ultrasonic waves of frequency range 0.5MHz to 20MHz are used for the testing of materials. The common range for testing metals is from 2MHz to 5MHz.
⮞Audible Frequency- 20Hz to 20KHz
⮞Ultrasonic Frequency- Greater than 20Khz
Type of Ultrasonic Waves–
There are various types of Ultrasonic waves, Some of them are elaborated below-
- Longitudinal Waves
- Transverse or Shear Waves
1. Longitudinal Waves–
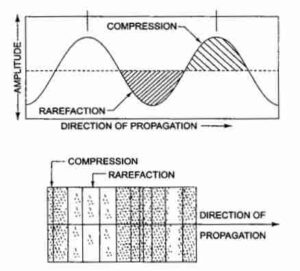
These are also called Compression Waves. In this type of ultrasonic wave, alternate compression and rarefaction zones are produced by the vibration of the particles parallel to the direction of propagation of the waves.
For a longitudinal ultrasonic wave, the plot of particle displacement versus distance of waves travels along with the resultant compression crest and rarefaction.
Fig. Schematic representation of a longitudinal wave-
2. Transverse or Shear Waves–
This type of ultrasonic wave is called a transverse or shear wave because the direction of particle displacement is at right angles or transverse to the direction of propagation.
For such a wave to travel through a material. It is necessary that each particle of material is strongly bound to its neighbors so that as one particle moves it pulls its neighbor with it.
Thus causing the ultrasonic energy to propagate through the material with a velocity that is about 50 percent that of the longitudinal velocity.
Fig. Schematic representation of transverse or Shear Wave-

For all practical purposes, transverse waves can only propagate in solids.
This is because the distance between molecules or atoms, the mean free path, is so great in liquids and gases that the attraction between them is not sufficient to allow one of them to move the other more than a fraction of its own movement and so the waves are rapidly attenuated.
The transmission of this wave type through a material is most easily illustrated by the motion of a rope as it is shaken.
Each particle of the rope moves only up and down, yet the waves move along the rope from the excitation point.
Why Ultrasonic Testing is used?
Ultrasonic testing is the most convenient and easy-to-navigate testing in the methods of Non-destructive testing.
Ultrasonic testing gives the exact size and depth of the flaws or defects and immediate results without damaging the object.
The suitability of many kinds of materials or metals is also a reason to use them in various sectors. Aerospace, mechanical industry, construction, medical. other sectors are known to use UT on a wide scale.
What Materials can be tested from Ultrasonic Testing?–
There are several materials, which can be tested by UT. The category of materials is given below-
- Metals
- Plastics
- Composites
- Ceramics
- Concrete
These are the materials, which can be tested through ultrasonic testing with reduced resolution in some of the materials.
Advantages of Ultrasonic Testing–
There are several advantages of ultrasonic testing, given below-
- It gives immediate results.
- It is suitable for the surface and sub-surface of the material.
- It is nom-hazardous testing, which means it doesn’t affect inspector health.
- It can measure the size, thickness, and depth of the flaws.
- Portable Equipment.
- It is suitable to test if one side of the material is available.
- Accurate detection is the main highlight.
- High sensitivity.
- High penetration capacity
Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Testing–
Here are some Disadvantages of Ultrasonic Testing–
- A skilled trained person is required.
- Rough, irregular shapes, thin, or non-homogeneous are considerably difficult to test.
- Requires oil or gel for the smoother transmission of ultrasonic waves.
- Equipment calibration is required.
- Cast iron and other coarse-grained materials are difficult to inspect.
Limitations of Ultrasonic Testing–
UT known is as the best in terms of accuracy and flexibility of testing, but it has some limitations, which should be known to you.
So, here are some limitations of UT-
- Metal inclusions may reduce, the sensitivity of sound waves.
- Paints need to be removed from the material surface, to perform the test smoothly.
- Complex geometry materials are difficult to inspect.
- Expensive equipment.
- Some materials are not receptive to Ultrasonic Waves.
Application of Ultrasonic Testing(UT)–
Here are some application UT, Given below-
- Inspection of large castings or objects.
- inspection of rails, roads, steel castings
- Thickness determination
- Ferrous and Non-Ferrous materials can be inspected(except. for some of the materials).
Standards and Codes of Ultrasonic Testing–
Useful specifications related to Ultrasonic testing-
1. BIS standards-
IS2417-1977– Glossary of terms relating to ultrasonic testing.
IS7281-7974– Immersed ultrasonic testing by the reflection method, using pulsed longitudinal waves, code of practice for.
IS7666-1975– Ultrasonic flaw detection of the ferritic casting of canon and low alloy steel, recommended procedure for.
2. British specifications-
BS2704-1966– Calibration blocks and recommendations for their use in ultrasonic flaw detection.
BS3889-1968– Ultrasonic testing of ferrous pipes(excluding cast).
BS3923-1968– Methods of ultrasonic examination of welds.
3. American Standards(ASTM)-
E113-74– Ultrasonic testing by resonance method.
E114-75– Ultrasonic pulse-echo straight beam testing by the contact method.
E127-75– Fabricating and checking of aluminum alloy, ultrasonic reference blocks.
4. French Specifications-
NF.A04.305.74– UT of steel plates, methods of testing, the definition of qualities.
NF.A04.3111.64– UT, calibration blocks, ferrous products, and steel pieces.
NF.A49.200.72– Seamless steel tubes for higher temperature and pressure application, testing by ultrasonic, classification according to quality, and various applications.
German Specifications(DIN)-
DIN- 54119– Non-Destructive testing- ultrasonic definitions
DIN- 54120– Non- destructive testing reference block and its use for the adjustment and control of ultrasonic echo equipment.
DIN- 54122– Non-destructive testing- reference block 2 and its use for the adjustment and control of pulse-echo equipment.
International Standard Organization(ISO)-
ISO-2400-72– Reference blocks for the calibration of equipment for UT of welds in the street.
Ultrasonic testing in Welds-
UT is most suitable for inspecting a welding object. It gives precise data about discontinuity or flaws.
Gas pipelines with high circumference pipes or object joints are preferred to inspect through UT and it also gives immediate data compared to other NDT methods, so the decision can be made quickly.
History of Ultrasonic Testing-
1931– Mulhauser registered a patent for using UT waves using two transducers to inspect the solids.
1929 & 1935– Sokolov studied the use of ultrasonic waves in detecting metal objects.
1940 & 1945– Firestone and Simons pulsed ultrasonic testing using the pulse-echo technique.
Conclusion–
Ultrasonic testing(UT) plays a major role in various industries and sectors, and preferred inspection method in the NDT sector.
As, I have shared most of the knowledge regarding UT, which you have read above. Hoping, you like the way it is presented.
If so, then forget to share with the needy one. It will help to educate one more person.
Thank you for reading, and bookmarking to know more about NDT.
Before you go, Here are your freebies all yours-
| Ultrasonic testing ppt |  |
Here are some of the related tests, you should consider to have a look…
Magnetic Particle Inspection(MPI)- All you need to know
Dye Penetrant Testing(DPT): Definition, Principle, Procedure, types
FAQs–
Q. What is ultrasonic testing used for?
Ans. A non-destructive method- UT uses high-frequency sound waves to inspect flaws in materials.
Q. What is the ultrasonic method?
Ans. A receiver generates high-voltage electrical pulses and a transducer converts those electrical pulses to high-frequency ultrasonic waves.
These waves propagate through the object in the form of sound waves.
If there is any defect or discontinuity in the path of sound waves, those waves reflect back to the receiver, Where the transducer converts Sound waves to electrical waves and displayed them on the screen.
Q. What are three types of ultrasonic inspection methods?
Ans. Three types of UT inspection methods are-
- Through transmission
- Pulse-echo method
- Resonance method
Q. What sort of materials can be tested with Ultrasonic Testing?
Ans. Name of the materials, which can be tested with UT-
- Metals
- Plastics
- Composites
- Ceramics
- Concrete
Q. Why does Ultrasonic Testing require applying a liquid on the test piece?
Ans. Couplant or liquid or gel is applied for the smoother transmission of Ultrasonic waves and this couplant prevents the losses of Ultrasonic waves while penetration.

Abhishek Tiwary is a blogger by passion and a Quality Engineer by profession. He completed his B.Tech degree in the year 2017. Now working in a reputed firm. He loves to share his knowledge with others.




